Understanding Male Anatomy: A Visual Guide to Sexual Function & Health
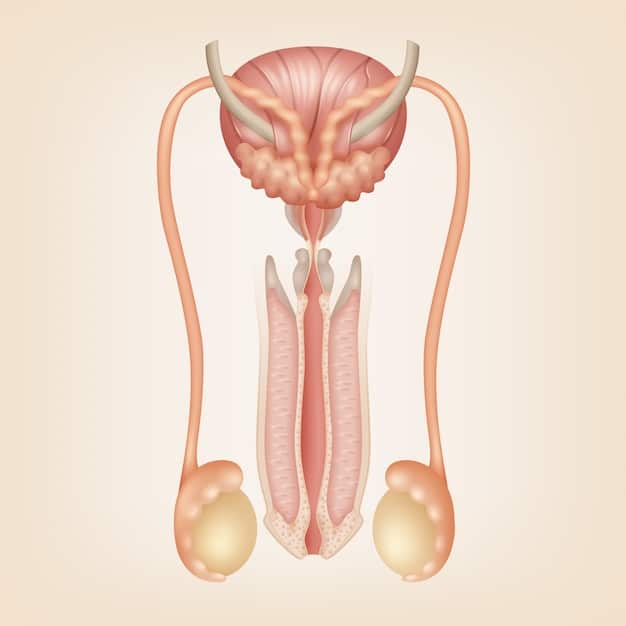
Understanding the Male Anatomy: A Visual Guide to Sexual Function and Health is crucial for sexual wellness. This guide provides a visual overview of male anatomy, enhancing understanding of sexual function and health management.
Gaining a comprehensive understanding of the male anatomy is essential for maintaining sexual health and overall well-being. This guide provides a visual exploration of the key components and their functions.
Understanding the Basics of Male Anatomy
The male anatomy is a complex and fascinating system, playing a vital role in sexual function and overall health. Understanding the Male Anatomy: A Visual Guide to Sexual Function and Health begins with grasping the fundamental components.
This section will cover the external and internal organs, providing a foundational knowledge essential for further exploration.
External Genitalia: A Closer Look
The external genitalia include the penis and the scrotum. The penis is the primary organ for sexual intercourse and urination, while the scrotum houses and protects the testicles.
Internal Organs: The Engine Room
The internal organs consist of the testicles, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands. Each organ plays a crucial role in sperm production, storage, and delivery.
- Testicles: Produce sperm and testosterone.
- Epididymis: Stores and matures sperm.
- Vas Deferens: Transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts.
- Seminal Vesicles: Produce fluid that nourishes and protects sperm.
These organs work in harmony to facilitate reproductive function. Proper understanding of their roles is essential for maintaining sexual health.
In summary, the basics of male anatomy involve both external and internal organs, each with specific functions. Understanding these basics sets the stage for comprehending sexual function and potential health issues related to these organs.
Detailed Examination of Sexual Function
Sexual function in males is a complex process involving various physiological and psychological factors. Knowing the various components ensures that Understanding the Male Anatomy: A Visual Guide to Sexual Function and Health is more than just looking at parts but involves how they function together.
This section will delve into the mechanisms behind erection, ejaculation, and the hormonal influences affecting sexual desire and performance.
Erection: The Role of Blood Flow and Nerves
Erection is achieved through increased blood flow to the penis, stimulated by nerve signals. Nitric oxide plays a crucial role in relaxing the smooth muscles of the penis, allowing blood to fill the erectile tissues.
Ejaculation: A Coordinated Muscular Action
Ejaculation involves the coordinated contraction of muscles in the vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and prostate gland, propelling semen through the urethra.
- Hormonal Influence: Testosterone plays a vital role in sexual desire and function.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can significantly impact sexual performance.
- Underlying Conditions: Diabetes, heart disease, and neurological disorders can affect sexual function.
Addressing both the physical and psychological aspects is important for resolving sexual dysfunction.
In conclusion, a detailed examination of sexual function reveals the interconnectedness of physiological and psychological elements. This understanding is vital for diagnosing and treating sexual dysfunctions effectively.
Common Health Issues Affecting Male Anatomy
Several health issues can impact the male anatomy, leading to various symptoms and potential complications. A clear understanding is key in Understanding the Male Anatomy: A Visual Guide to Sexual Function and Health and diagnosing various ailments.
This section will explore some of the most common conditions, including prostatitis, erectile dysfunction, and testicular cancer.
Prostatitis: Inflammation of the Prostate Gland
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland, often caused by bacterial infection. Symptoms include pelvic pain, urinary problems, and sexual dysfunction.
Erectile Dysfunction: Challenges in Achieving or Maintaining Erection
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse. It can be caused by physical or psychological factors.

- Testicular Cancer: A malignant tumor in one or both testicles.
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Enlargement of the prostate gland, causing urinary symptoms.
- Peyronie’s Disease: Formation of fibrous scar tissue inside the penis, causing curved, painful erections.
Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing these conditions and improving overall health.
In summary, being aware of common health issues affecting the male anatomy is essential for early detection and effective management. Regular check-ups and prompt medical attention can significantly improve outcomes.
Maintaining Optimal Sexual Health: Practical Tips
Maintaining optimal sexual health involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and practicing good hygiene. These practices, when understood in conjunction with Understanding the Male Anatomy: A Visual Guide to Sexual Function and Health, can improve health and reduce potential ailments.
This section outlines practical tips for men to maintain their sexual health and prevent common issues.
Adopting a Healthy Lifestyle
A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are crucial for overall health, including sexual function. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also improve sexual health.
Practicing Good Hygiene
Regularly cleaning the genital area can prevent infections and maintain good hygiene. Proper hygiene also involves wearing breathable clothing and avoiding harsh soaps.
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine medical examinations can detect potential issues early.
- Safe Sex Practices: Using condoms during sexual intercourse can prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and counseling can help reduce stress and improve sexual function.
- Open Communication: Discussing sexual health concerns with a partner or healthcare provider can lead to better understanding and solutions.
Taking proactive steps to maintain sexual health can significantly improve quality of life and prevent potential issues.
In conclusion, maintaining optimal sexual health requires a combination of healthy habits, hygiene practices, and proactive medical care. By following these practical tips, men can improve their sexual well-being and prevent common issues.
The Psychological Impact of Sexual Health
Sexual health is not only a physical matter but also significantly impacts psychological well-being. The various physical parts of sexual health tie in with Understanding the Male Anatomy: A Visual Guide to Sexual Function and Health, making a holistic appreciation.
This section delves into the psychological aspects of sexual health, including the effects of sexual dysfunction on self-esteem, relationships, and overall mental health.
Self-Esteem and Body Image
Sexual dysfunction can lead to decreased self-esteem and negative body image. Men may feel inadequate or embarrassed, affecting their confidence and self-worth.
Relationship Dynamics
Sexual health issues can strain relationships, leading to misunderstandings, frustration, and intimacy problems. Open communication and mutual understanding are crucial for navigating these challenges.
- Mental Health: Anxiety, depression, and stress can be both the cause and consequence of sexual dysfunction.
- Seeking Support: Counseling, therapy, and support groups can provide valuable resources for coping with the psychological impact of sexual health issues.
- Positive Outlook: Maintaining a positive attitude and focusing on overall well-being can improve mental health and sexual function.
Addressing the psychological aspects of sexual health is essential for holistic well-being.
In summary, the psychological impact of sexual health cannot be overlooked. Recognizing and addressing these psychological factors is crucial for improving overall quality of life.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 💪 Anatomy Basics | Understanding male anatomy is essential for sexual health. |
| ❤️ Sexual Function | Blood flow and nerves are crucial for erection and ejaculation. |
| 🩺 Common Issues | Conditions like prostatitis and ED can affect male anatomy. |
| 🧠 Psychological Impact | Sexual health affects self-esteem and relationships. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The main parts include the penis, testicles, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and prostate gland. Each plays a unique role in reproduction and sexual function.
Maintain good health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and good hygiene. Regular medical check-ups and safe sex practices are also recommended.
Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection. It’s addressed via lifestyle changes, medication, therapy, or surgery after considering the anatomy.
Stress can negatively impact sexual desire and performance. Managing stress through relaxation techniques or counseling can improve sexual function.
Understanding male anatomy helps in early detection of issues like cancer and ED. That improves sexual, reproductive, and psychological comfort.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the male anatomy and maintaining sexual health are vital for overall well-being. Understanding the Male Anatomy: A Visual Guide to Sexual Function and Health provides the essential knowledge for men to take proactive steps in maintaining their health.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle, practicing good hygiene, and seeking timely medical care, men can ensure a fulfilling and healthy sexual life. Addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of sexual health is key to a better quality of life.





